The number of Medicare Advantage (MA) Special Needs Plans (SNPs) has surged in enrollment, growing its member base by more than twofold from 2020 to 2022. This influx of new members has generated an opportunity to achieve better health outcomes for targeted groups of people and provide members with tailored care solutions.
These plans are not only popular with members, but they also appear to be associated with positive consequences, such as decreases in all-cause hospitalizations. Nevertheless, increased enrollment is accompanied by increased operational challenges, as the high-touch model of member management continues to scale.
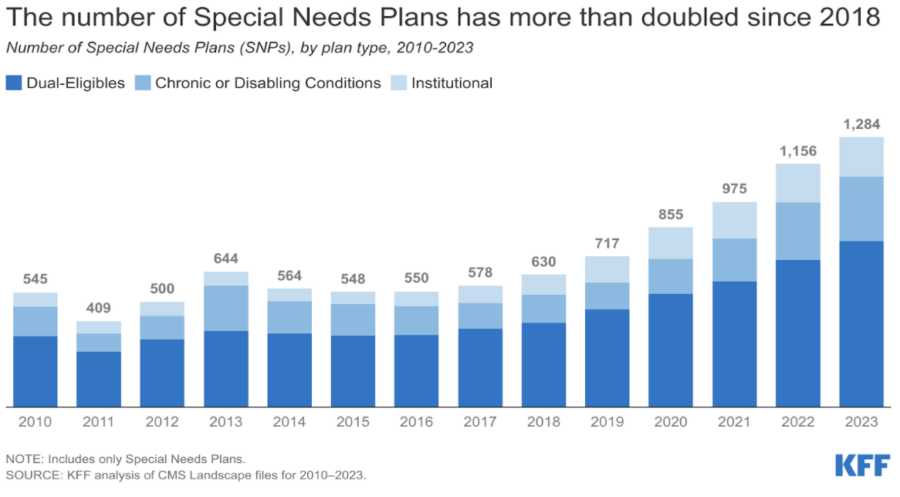
What are Medicare Advantage Special Needs Plans?
A Special Needs Plan (SNP) provides benefits and services to people with specific diseases, certain healthcare needs, or who also have Medicaid. SNPs tailor their benefits, provider choices, and list of covered drugs to best meet the specific needs of the groups they serve.
For example, there are SNPs for those with chronic conditions (C-SNPs), individuals who are dually eligible (D-SNPs), and people who require institutional care (I-SNPs).
Since 2018, the number of C-SNPs has grown rapidly, mainly targeting those with diabetes, heart disease, and lung issues. These specialized plans offer benefits to improve long-term care such as increased coordination between doctors and providers, or discounts on medications/medical equipment. They also make it easier for people who are living with complex or chronic conditions to manage the long-term care services they need to live in the home and community.
What are the 3 Types of Medicare Advantage Special Needs Plans?
SNPs come in three types, each with its own eligibility requirements and coverage:
- Chronic Condition Special Needs Plans (C-SNPs) offer specialized coverage for people with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, end-stage renal disease, respiratory disease, and several other chronic conditions. While less common, some C-SNPs cover conditions such as chronic mental illnesses, dementia, and HIV/AIDS.
- Dual Eligible Special Needs Plans (D-SNPs) create coordinated coverage for people eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
- Institutional Special Needs Plans (I-SNPs) are for people who live in an institution, such as a nursing home, or who require institutional-level nursing care at home.
What are the Benefits of Medicare Advantage Special Needs Plans?
Special Needs Plans provide targeted benefits that address the specific needs of individuals with chronic conditions or unique circumstances. They offer valuable support for aging in place, enhance engagement through in-home services, and present a cost-effective option for comprehensive care. The following sections highlight how SNPs can improve the quality of life for members.
Support People as they Age in Place
In 2023, in-home support services (IHSS) became the fastest-growing benefit among a newly expanded set of supplemental options for MA members. These services support activities of daily living (e.g., bathing and dressing) and help people who are aging in place or living with complex needs. Members can also enlist help for housekeeping or personal care services.
Engage People in Their Homes
According to ATI Advisory, some in-home services produced unintended but positive, consequences.
For example, there were numerous instances where the presence of a home visitor reduced the hospitalization rate and incidence of in-home falls among members.
It might be the case that the presence of an engaged, empathetic visitor can achieve some of the benefits that MA plans were designed to deliver without the need for specialized equipment or skilled nursing.
Cost-Effective Option for Care
We’re seeing plans take advantage of preventative interventions including ADL support through homemaker and home health aide services, caregiver support and respite services, home safety evaluations and home modifications, healthy meal programs post-hospitalization, and transportation for both medical and non-medical appointments.
The good news is these interventions work when accessible and managed correctly. Johns Hopkins School of Nursing has more than a decade of research from its Community Aging in Place-Advancing Better Living for Elders (CAPABLE) program that shows that these types of benefits work to reduce health disparities, hospitalizations, and nursing home days.
Research has shown that services like nutrition, home safety, and medication management offered through CAPABLE programs have provided more than six times the return on investment. Roughly $3,000 in program costs per participant yielded more than $30,000 in savings in medical costs driven by reductions in both inpatient and outpatient expenditures.
Challenges to Medicare Advantage Special Needs Plans
Special Needs Plans often face obstacles that can affect effectiveness and continuity of care. Key challenges include persistent staffing shortages which impact service delivery, and the need for innovative solutions to address these gaps. Preparing for changes in healthcare delivery is essential for adapting to evolving needs. Here are some challenges and potential solutions.
Persistent Staffing Shortages
One significant challenge is the shortage of post-acute and in-home healthcare providers. While it is crucial to allocate funding for the IHSS program, simply providing funds is insufficient if there are no available professionals.
Solutions Needed to Fill Gap
The burden is on health plans and providers to seek out innovative solutions to address this issue and help close the gap. Increasingly, health organizations are turning to technology to solve some of the complex challenges related to moving care from traditional acute settings and into homes and communities.
For many, the investment in key tools and technologies can increase efficiencies and improve the capacity of current staff, and help team members feel that their work is impactful, meaningful, and helpful for members and patients.
Preparing for Shift in Healthcare Delivery
Some of the site-of-care shifts that occurred during the pandemic due to clinical necessity will forever change the way care is delivered. The upward trend around the delivery of in-home health services is expected to continue led, in part, by consumer demand and an aging population. Policy changes, virtual and digital innovations, and the shift to lower-cost settings will all contribute to a restructuring of the current system of care. MA leaders should prepare now to manage this ongoing shift in healthcare delivery.
Resources
Find more information about SNPs in the following reports and articles:
- CMS Guide to Special Needs Plans
- CMS Special Needs Plan Data
- Special Needs Plans are on the Rise: 6 States Lead Enrollment
- Integrated Care Resource Center

MA Plans are Booming:
How Will You Stay Competitive?
Download our report “Home Benefits Surge in Popularity Among Medicare Advantage Plans” to learn more about leveraging supplemental benefits to increase member satisfaction, retention and STARs.






